Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1: The Solid State - Complete Study Notes
Chapter Index
📚 Complete Topic Coverage
- General Characteristics of Solid State
- Amorphous and Crystalline Solids
- Classification of Crystalline Solids
- Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells
- Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell
- Close Packed Structures
- Packing Efficiency
- Calculations Involving Unit Cell Dimensions
- Imperfections in Solids
- Electrical Properties
- Magnetic Properties
- Important Formulas Summary
- Previous Year Questions Pattern
- Exam Tips & Quick Revision

📖 Chapter Overview
The Solid State chemistry का एक fundamental chapter है जो matter की solid state के बारे में detailed study करता है। इस chapter में हम सीखते हैं कि solids कैसे organize होते हैं, उनकी different types क्या हैं, और उनके properties कैसे determine होती हैं।
यह chapter NCERT chemistry syllabus का important part है क्योंकि यहाँ से हमेशा 3-4 marks के questions आते हैं। Crystal structures, packing efficiency, और unit cell calculations के concepts बहुत crucial हैं।
🎯 Key Concepts Overview
मुख्य Topics जो Cover करेंगे:
- Solid state की characteristics और classification
- Crystal lattice और unit cell की geometry
- Different packing arrangements और efficiency calculations
- Solid materials की electrical और magnetic properties
- Crystal defects और imperfections
- Numerical problems solving techniques
📝 Detailed Topic-wise Notes
1. General Characteristics of Solid State
Solid State के मुख्य Features:
Solids की कुछ distinct characteristics होती हैं जो उन्हें liquids और gases से अलग बनाती हैं।
Key Characteristics:
- Definite Shape और Volume: Solids का fixed shape और volume होता है
- Strong Intermolecular Forces: Particles के बीच strong attractive forces होती हैं
- Low Compressibility: Solids को compress करना difficult होता है
- Ordered Arrangement: Particles systematic arrangement में होते हैं
- High Density: Generally solids का density liquids से ज्यादा होता है
Real-life Example: Ice cubes का shape और volume fixed रहता है, chahe container कैसा भी हो।
2. Amorphous and Crystalline Solids
यह topic बहुत important है क्योंकि यहाँ से हमेशा conceptual questions आते हैं।
Crystalline Solids:
- Long-range order में arranged particles
- Sharp melting point होता है
- Anisotropic properties - different directions में different properties
- Regular geometric shapes बनते हैं
Examples: NaCl, Diamond, Quartz
Amorphous Solids:
- No long-range order - random arrangement
- Range of melting point होता है
- Isotropic properties - सभी directions में same properties
- Irregular shapes बनते हैं
Examples: Glass, Rubber, Plastic
Memory Trick: Crystalline = Clear arrangement, Amorphous = Arranged Messily
3. Classification of Crystalline Solids
Crystalline solids को bonding के basis पर classify करते हैं:
Ionic Solids:
- Electrostatic forces hold करती हैं
- High melting points
- Electrical conductors when molten
- Examples: NaCl, CsCl, ZnS
Covalent/Network Solids:
- Covalent bonds में connected
- Very high melting points
- Generally insulators
- Examples: Diamond, Silicon carbide
Molecular Solids:
- Van der Waals forces या hydrogen bonding
- Low melting points
- Soft और easily compressible
- Examples: Ice, Solid CO₂
Metallic Solids:
- Metallic bonding - electron sea model
- Good conductors
- Malleable और ductile
- Examples: Cu, Fe, Al
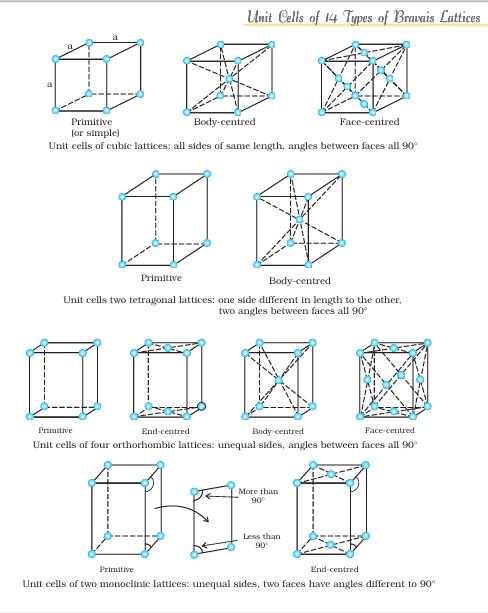
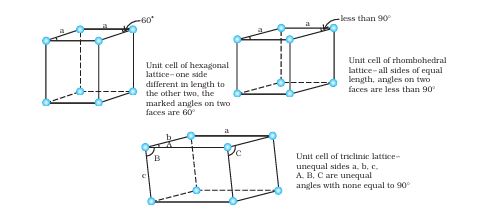
4. Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells
यह section numerical problems के लिए बहुत important है।
Crystal Lattice:
Crystal lattice एक 3D arrangement है जो infinite extend करता है। यह imagine करो जैसे एक 3D chess board हो।
Unit Cell:
Unit cell lattice का smallest repeating unit है।
Types of Unit Cells:
Primitive/Simple Cubic:
- Atoms केवल corners पर
- Coordination number = 6
- Packing efficiency = 52.4%
Body-Centered Cubic (BCC):
- Corners + center में atoms
- Coordination number = 8
- Packing efficiency = 68%
Face-Centered Cubic (FCC):
- Corners + face centers में atoms
- Coordination number = 12
- Packing efficiency = 74%
5. Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell
यह calculation-based topic है जो exams में frequently आता है।
Calculation Formula:
Corner atoms contribution: Each corner atom = 1/8 atom
Face-center atoms contribution: Each face atom = 1/2 atom
Body-center atoms contribution: Each body atom = 1 complete atom
For Different Unit Cells:
Simple Cubic:
- 8 corners × (1/8) = 1 atom per unit cell
BCC (Body-Centered Cubic):
- 8 corners × (1/8) + 1 body center = 2 atoms per unit cell
FCC (Face-Centered Cubic):
- 8 corners × (1/8) + 6 faces × (1/2) = 4 atoms per unit cell
Memory Trick: SBC = 1, 2, 4 (Simple, Body, Face)
6. Close Packed Structures
Close packing structures को समझना बहुत जरूरी है।
Types of Close Packing:
Cubic Close Packing (CCP):
- FCC structure same होता है
- ABCABC type layering
- Coordination number = 12
Hexagonal Close Packing (HCP):
- ABAB type layering
- Coordination number = 12
- Same packing efficiency as CCP
Voids in Close Packing:
Tetrahedral Voids:
- 4 spheres surround करते हैं
- Number = 2n (n = number of spheres)
Octahedral Voids:
- 6 spheres surround करते हैं
- Number = n (n = number of spheres)
7. Packing Efficiency
यह topic numerical problems के लिए crucial है।
Packing Efficiency Formula:
Packing Efficiency = (Volume occupied by atoms / Total volume of unit cell) × 100
For Different Structures:
Simple Cubic Packing:
- Packing Efficiency = 52.4%
- Formula derivation: π/6 × 100
BCC Packing:
- Packing Efficiency = 68%
- Formula derivation: (√3π/8) × 100
FCC/CCP Packing:
- Packing Efficiency = 74%
- Formula derivation: (π√2/6) × 100
Memory Trick: SBC packing = 52, 68, 74%
8. Calculations Involving Unit Cell Dimensions
Important Relationships:
For Simple Cubic:
- a = 2r (a = edge length, r = atomic radius)
For BCC:
- a√3 = 4r
- r = (a√3)/4
For FCC:
- a√2 = 4r
- r = (a√2)/4
Density Calculation:
ρ = (Z × M)/(N₀ × a³)
Where:
- ρ = density
- Z = number of atoms per unit cell
- M = molar mass
- N₀ = Avogadro's number
- a = edge length
9. Imperfections in Solids
Real crystals में defects होते हैं जो properties को affect करते हैं।
Types of Defects:
Point Defects:
- Vacancy defect: Atom missing from lattice site
- Interstitial defect: Extra atom in interstitial space
Stoichiometric Defects:
- Schottky defect: Equal number of cation-anion pairs missing
- Frenkel defect: Cation moves to interstitial site
Non-stoichiometric Defects:
- Metal excess defect
- Metal deficiency defect
10. Electrical Properties
Solids की electrical conductivity के basis पर classification:
Conductors:
- High conductivity (10⁴ to 10⁷ ohm⁻¹m⁻¹)
- Examples: Metals like Cu, Al
Semiconductors:
- Moderate conductivity (10⁻⁶ to 10⁴ ohm⁻¹m⁻¹)
- Temperature dependent conductivity
- Examples: Si, Ge
Insulators:
- Very low conductivity (<10⁻⁶ ohm⁻¹m⁻¹)
- Examples: Wood, Glass
11. Magnetic Properties
Types of Magnetic Behavior:
Diamagnetic:
- Weakly repelled by magnetic field
- All electrons paired
- Examples: NaCl, C₆H₆
Paramagnetic:
- Weakly attracted by magnetic field
- Unpaired electrons present
- Examples: O₂, Cu²⁺
Ferromagnetic:
- Strongly attracted by magnetic field
- Examples: Fe, Ni, Co
📊 Important Formulas Summary Table
| Property | Formula | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Packing Efficiency (SC) | π/6 × 100 = 52.4% | Simple cubic calculations |
| Packing Efficiency (BCC) | (√3π/8) × 100 = 68% | BCC structure problems |
| Packing Efficiency (FCC) | (π√2/6) × 100 = 74% | FCC structure problems |
| Density | ρ = (Z × M)/(N₀ × a³) | Unit cell mass calculations |
| Edge length (BCC) | a = (4r)/√3 | BCC dimensions |
| Edge length (FCC) | a = (4r)/√2 | FCC dimensions |
| Tetrahedral voids | Number = 2n | Void calculations |
| Octahedral voids | Number = n | Void calculations |
🎯 Previous Year Questions Types
Commonly Asked Question Patterns:
1. Conceptual Questions (2-3 marks):
- Difference between crystalline और amorphous solids
- Types of unit cells और their characteristics
- Classification of solids based on bonding
2. Numerical Problems (3-5 marks):
- Packing efficiency calculations
- Density और unit cell parameter relations
- Number of atoms in unit cell
3. Structure-based Questions:
- Close packing arrangements
- Coordination number determinations
- Void calculations
Important Numerical Types:
- Unit cell edge length से atomic radius find करना
- Density से unit cell parameters calculate करना
- Packing efficiency की calculations
- Avogadro's number based problems
💡 Tips for Exam Preparation
Study Strategy:
Conceptual Clarity:
- Diagrams बनाकर unit cells को visualize करें
- Real examples के साथ concepts को relate करें
- Classification को tabular form में याद करें
Numerical Practice:
- Formula sheet बनाएं और regularly revise करें
- Step-by-step approach follow करें numerical problems में
- Units का special ध्यान रखें calculations में
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Coordination number और number of atoms को confuse न करें
- Packing efficiency formulas को properly memorize करें
- Density calculations में units का conversion सही करें
Memory Techniques:
For Packing Efficiency:
"Simple Boys Face" = 52, 68, 74%
For Coordination Numbers:
"Simple = 6, Body = 8, Face = 12"
For Unit Cell Atoms:
"1-2-4 sequence" (Simple-BCC-FCC)
⚡ Quick Revision Points
Key Points to Remember:
- Crystalline vs Amorphous: Order, melting point, anisotropy
- Unit Cell Types: Simple (1), BCC (2), FCC (4) atoms
- Packing Efficiency: SC < BCC < FCC
- Close Packing: CCP = FCC, coordination number = 12
- Defects: Schottky (both ions), Frenkel (cation only)
- Electrical Properties: Conductor > Semiconductor > Insulator
- Magnetic Properties: Diamagnetic (paired), Paramagnetic (unpaired)
Formula Quick Check:
- Density: ρ = ZM/(N₀a³)
- BCC edge: a = 4r/√3
- FCC edge: a = 4r/√2
- Voids: Tetrahedral = 2n, Octahedral = n
Last-Minute Tips:
- Practice numerical problems daily
- Make flow charts for classifications
- Revise formulas with derivations
- Solve previous year papers for pattern understanding
यह chapter board exams में scoring है अगर concepts clear हों और numerical practice sufficient हो। Regular practice और conceptual clarity के साथ इस chapter से अच्छे marks secure कर सकते हैं।
Meta Description: Complete Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State Notes in Hindi English mixed language. Covers NCERT syllabus with formulas, examples, and exam tips for board preparation.
